If you’re working with large workbooks in Excel, you may find it useful to know the size of each worksheet within the workbook. This information can help you identify which worksheets are taking up the most space and optimize your file for better performance.
This post will guide you how to check the size of each worksheet of workbook using VBA code in Excel. How do I get the data size of each worksheet in a workbook in Excel 2013/2016/2019/365.
Assuming that you have a Workbook which contains multiple worksheet, and you want to know the data size of each worksheet in the current workbook. This post will show two methods with you.
Table of Contents
Method1: Get the Data Size of Each Worksheet by Manually
You can get the data size of each worksheet one by one manually, and you just need to copy the contents of an Excel worksheet in your workbook, and then create a new workbook, and pasted the content into sheet1 in the new workbook, and then save the new workbook to a windows folder. Then you can get the size of this newly workbook.
You can repeat the above steps to get the data sizes of other worksheets one by one in your workbook.
Method2: Get the Data Size of Each Worksheet via VBA Macro
If you want to quickly get the data size of each worksheet in your current workbook, you can use an Excel VBA macro to accomplish it. Just do the following steps:
Step1: open your excel workbook and then click on “Visual Basic” command under DEVELOPER Tab, or just press “ALT+F11” shortcut.
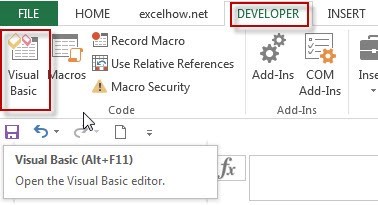
Step2: then the “Visual Basic Editor” window will appear.
Step3: click “Insert” ->”Module” to create a new module.
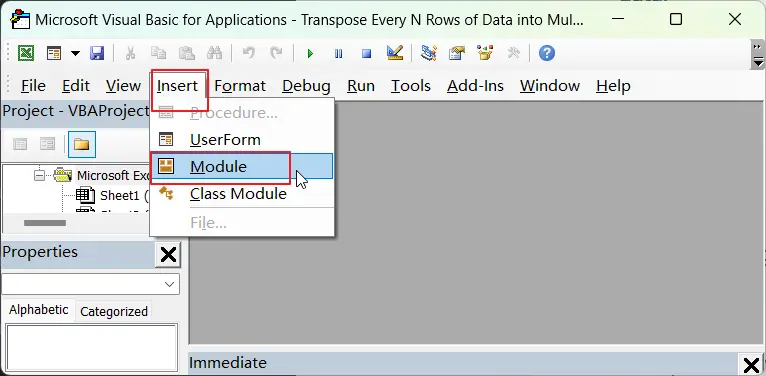
Step4: paste the below VBA code into the code window. Then clicking “Save” button.
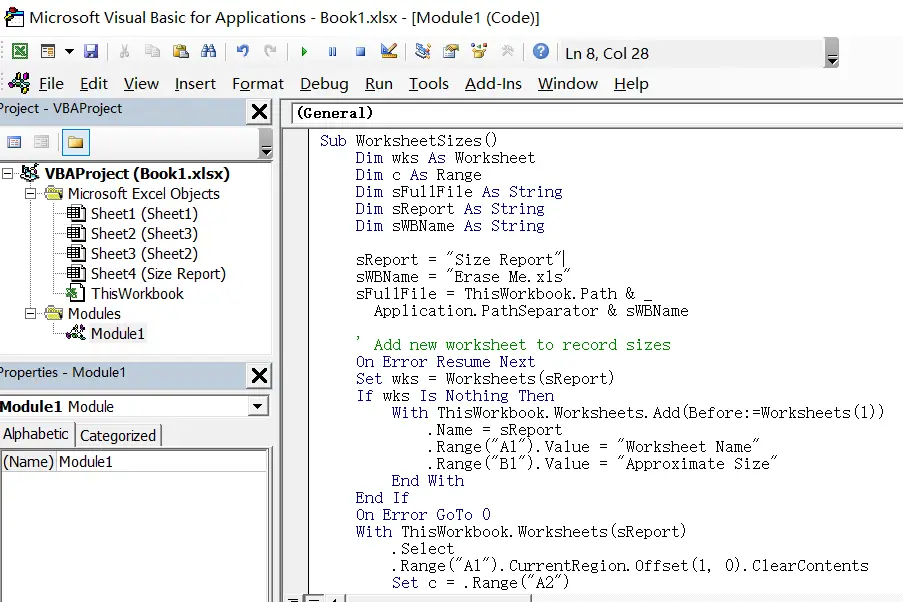
Sub WorksheetSizes_excelhow()
Dim wks As Worksheet
Dim c As Range
Dim sFullFile As String
Dim sReport As String
Dim sWBName As String
sReport = "Size Report"
sWBName = "tmp.xls"
sFullFile = ThisWorkbook.Path & _
Application.PathSeparator & sWBName
' Add new worksheet to record sizes
On Error Resume Next
Set wks = Worksheets(sReport)
If wks Is Nothing Then
With ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Add(Before:=Worksheets(1))
.Name = sReport
.Range("A1").Value = "Worksheet Name"
.Range("B1").Value = "Approximate Size"
End With
End If
On Error GoTo 0
With ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(sReport)
.Select
.Range("A1").CurrentRegion.Offset(1, 0).ClearContents
Set c = .Range("A2")
End With
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
' Loop through worksheets
For Each wks In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets
If wks.Name <> sReport Then
wks.Copy
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs sFullFile
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
c.Offset(0, 0).Value = wks.Name
c.Offset(0, 1).Value = FileLen(sFullFile)
Set c = c.Offset(1, 0)
Kill sFullFile
End If
Next wks
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End Sub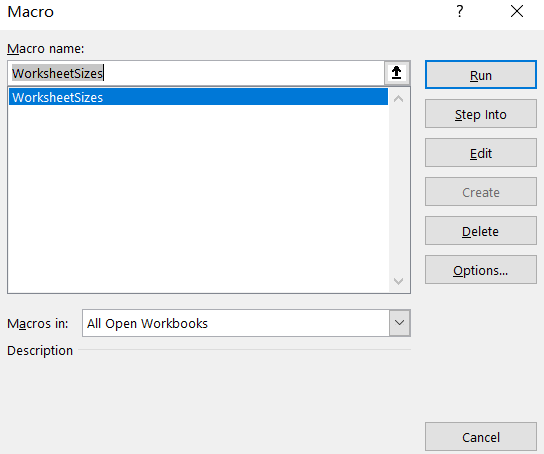
Step6: let’s see the last result:
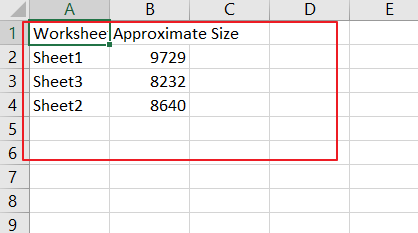
Video: Get the Data Size of Each Worksheet
This video will show you how to use VBA code to get the data size of each worksheet in a workbook.
Conclusion
With the above VBA code, you can quickly and easily retrieve the size of each worksheet in your workbook and take necessary steps to manage the file size in Microsoft Excel.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.